Are you in the financial services industry in Malaysia? If you are any of the following, you’ve probably heard of the Bank Negara of Malaysia’s Risk Management in Technology (RMiT) regulation that is applicable to:
- Licensed banks
- Licensed investment banks
- Licensed Islamic banks
- Licensed insurers including professional reinsurers
- Licensed takaful operators including professional retakaful operators
- Prescribed development financial institutions
- Approved issuer of electronic money
- Operator of a designated payment system
The Risk Management in Technology (RMiT) policy was created to ensure Malaysian financial institutions properly manage their cyber-risk exposure by establishing the necessary risk frameworks, governance structures, policies, and procedures.
With the perpetually increasing use of technology in the financial services industry, the Central Bank of Malaysia saw it necessary to put in place this framework to minimize operational disruptions and maintain confidence in the system from outside threat.
The published RMiT policy covers the following six domains:
- Governance
- Technology Risk Management
- Technology Operations Management
- Cybersecurity Management
- Technology Audit
- Internal Awareness & Training
All financial organizations within Malaysia are required to implement the minimum prescribed standards in this policy to prevent the exploitation of weak links in interconnected networks and systems that may cause detriment to other financial institutions and the wider financial systems.
Ultimately, the framework is structured such that larger and more complex financial institutions will be able to demonstrate the risk management practices above and beyond the minimally accepted standards that are commensurate with the level of risk that they pose.
All requirements in the policy document are specified pursuant to the following:
- Sections 47(1) and 143(2) of the Financial Services Act 2013 (FSA);
- Sections 57(1) and 155(2) of the Islamic Financial Services Act 2013 (IFSA);
- Sections 41(1) and 116(1) of the Development Financial Institutions Act 2002 (DFIA).
All guidance in this policy document is issued pursuant to the following:
- Section 266 of the FSA;
- Section 277 of the IFSA;
- Section 126 of the DFIA;
The policy went into effect on January 1, 2020, and requires companies that are under the scope of RMiT to demonstrate compliance with this policy via an independent external service provider (ESP). The independent ESP shall review the comprehensiveness of the risk assessment performed by the financial institution and validate the adequacy of the control measures implemented or to be implemented.
Though the requirement has been in effect for eight months, there has been limited public information regarding entities that have or have not been fined due to examples of non-compliance. The longer the compliance is active we expect to see more examples of non-compliance made public to better understand what kind of enforcement actions may be taken.
For more detailed information on the RMiT, download the policy document here.
Achieve Compliance with LogRhythm
The LogRhythm SIEM Platform enables your organization to meet many RMiT guidelines by collecting, managing, and analyzing log data. LogRhythm AI Engine (AIE) rules, alarms, reports, investigations, and general SIEM functionality also help your organization satisfy certain risk management elements outlined by the RMiT.
The suite has been built using LogRhythm’s Consolidated Compliance Framework (CCF) content, which cross-maps numerous globally accepted frameworks to demonstrate compliance across multiple jurisdictions which will enable organizations to streamline their compliance efforts. Additionally, LogRhythm’s compliance modules are updated as frameworks evolve and are clarified over time, so customers have up-to-date compliance content.
LogRhythm provides Dashboards that are designed to enable efficient monitoring of RMiT compliance and best practices. In the dashboard below, LogRhythm enabled widgets for monitoring RMiT Control Support. Figure 1 shows the real-time compliance status of control requirements that are related to cybersecurity management from RMiT Compliance.
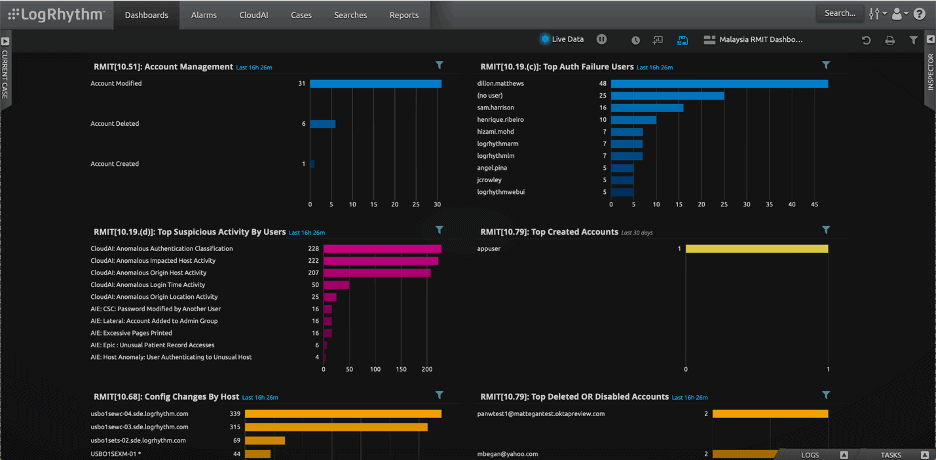
In Figure 2, LogRhythm shows the real-time compliance status of control requirements that are related to technology operation management from RMiT Compliance.
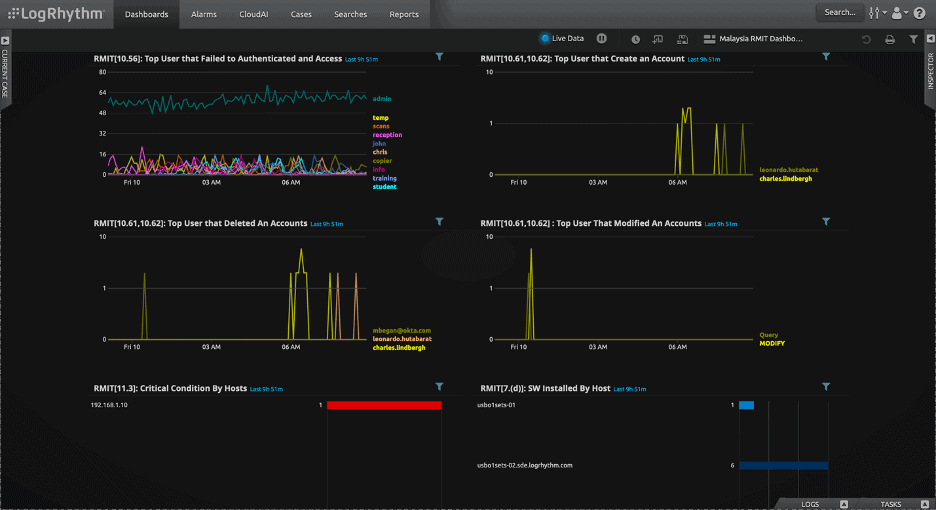
And in Figure 3, LogRhythm shows the real-time compliance status of control requirements that are related to technology risk management from RMiT Compliance. This interface can easily be modified with new widgets by clicking the Add Widget button in the top menu of the UI.
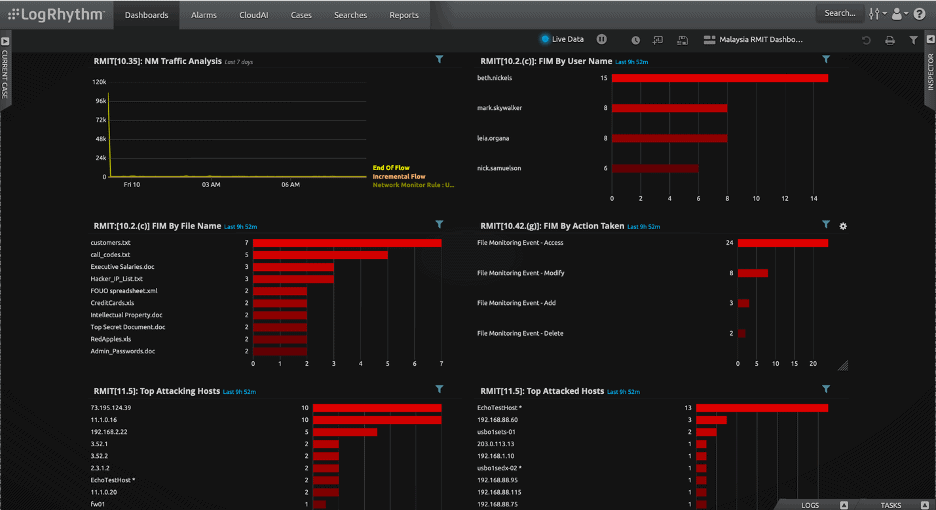
LogRhythm uses RMiT AI Engine (AIE) rules to detect use cases that breach RMiT compliance and then trigger the alarm with risk-based priority (RBP). Once the RMiT related alarm is triggered, it will notify analysts and initiate the security orchestration automation response (SOAR) workflow, which will shorten time to response (TTR) of an incident.
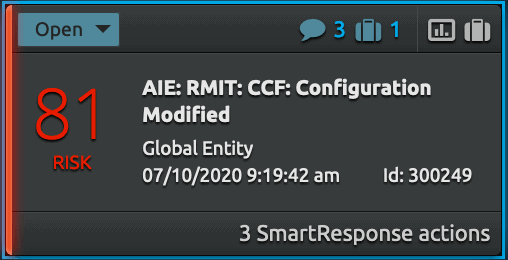
The alarm integration provides seamless continuity across the end-to-end threat detection and response workflow. Figure 4 shows a sample RMiT Alarm which is related to configuration modification, and it also shows there are three SmartResponse™ actions (a LogRhythm SOAR component).
An analyst is able to drill down further for complete visibility on a triggered alarm which can be seen in Figure 5. Alarm Drill Down Analyze View gives analysts a deeper understanding such as information on which user triggered the alarm, his/her role in the company, his/her profile, the host that triggered the alarm, and the type of log source which detects suspicious activity such as configuration being modified.
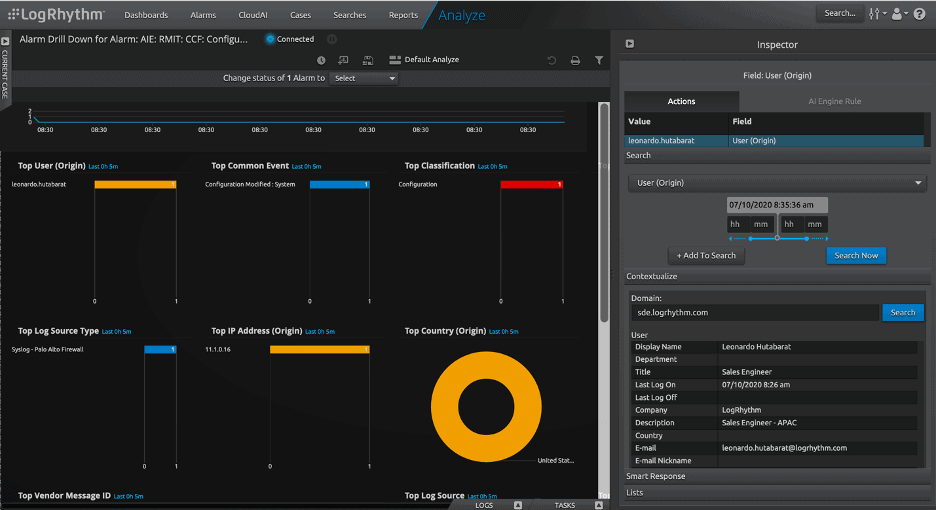
LogRhythm understands that organizations may be at different points of compliance maturity, so the RMiT module gives organizations the flexibility to realize value at any point along that maturity scale. LogRhythm augments RMiT requirements and decreases the cost to meet others through prebuilt content and functionality.
Offering a level of customization, RMIT can also be used with advanced LogRhythm functionality such as NetMon, TrueIdentity™, SysMon, threat research content, and case management.
If you’re interested in understanding how LogRhythm can help you achieve compliance within the financial industry, contact us to learn more about our full stack of security solutions.
