Are You Prepared for Ransomware?
Ransomware is and has been a scourge upon our houses for a while now. To quote The Ransomware Threat: A How-To Guide on Preparing for and Detecting an Attack Before it’s Too Late, “2016 is the year ransomware will hold America hostage. With the FBI estimating that losses to be incurred in 2016 will top $1 billion, how can you be sure you’re ready to face the ransomware threat?”
Using LogRhythm to Thwart a Ransomware Attack
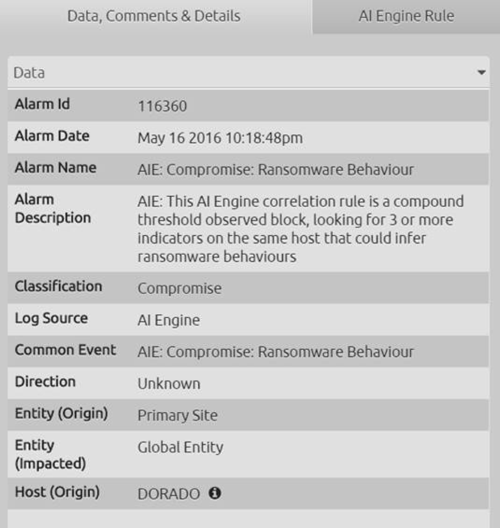
Figure 1. AI Engine Alarm on Ransomware Behavior
Imagine you’re going about your day, and then you see it—an alarm in the LogRhythm SIEM Platform that ransomware has been detected by the AI Engine. But how? And what has been detected?
Detecting the Ransomware Threat
First, you click the Inspector panel within the LogRhythm WebUI. There you see the alarm metadata.
Click images to expand
Figure 2. The Ransomware Behavior Alarm Metadata
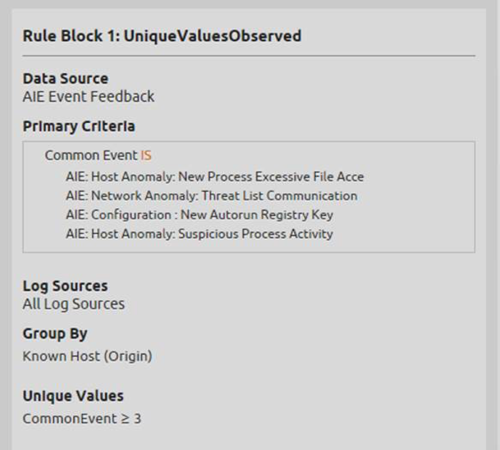
Figure 3. The Ransomware Behavior AI Engine Correlation Rule Logic
You are now able to see that the alarm description explains how this works—a threshold rule looking for three or more ransomware indicators on the same host. You can also see that Dorado is the host detected as having ransomware.
Looking at the AI Engine rule tab, you can see the actual rule logic. You’re using a powerful feature of the LogRhythm AI Engine called “AI Engine Feedback.” This means that not only can LogRhythm’s correlation detect and generate events, but it can also use those same self-generating events as part of an AI Engine rule. The specific AI Engine events in this rule include three or more of the following AI Engine-generated events on the same host:
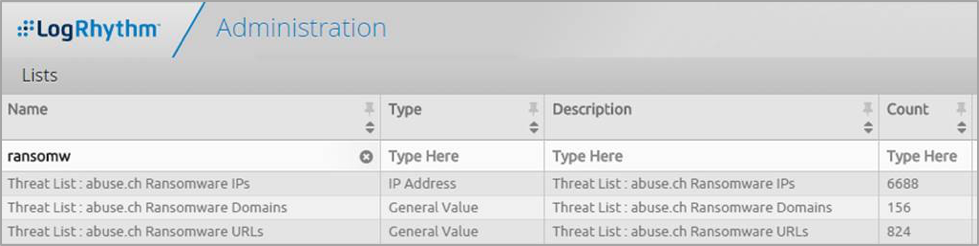
Threat Lists Communications with Known Ransomware Hosts
Figure 4. Threat List Communications with Known Ransomware Hosts
Figure 5. Ransomware Threat Lists
You can use LogRhythm NetMon to monitor all east/west and north/south traffic. This alarm also includes another powerful feature of the LogRhythm SOAR security solution — SmartResponse™. In this example, Palo Alto firewalls have the ability to remediate the action by either blocking the source, destination user or host.
Try NetMon Freemium.
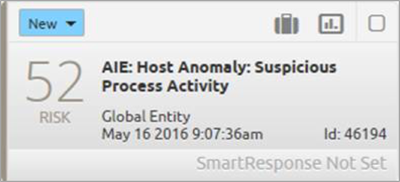
Suspicious Process Activity
Figure 6. Suspicious Process Activity
Using either LogRhythm endpoint monitoring, native OS auditing or third-party endpoint agents, you can then look for and alert on suspicious administrative processes that are not normally seen, but are known to be used as part of ransomware behavior. LogRhythm facilitates this through a wide range of inputs.
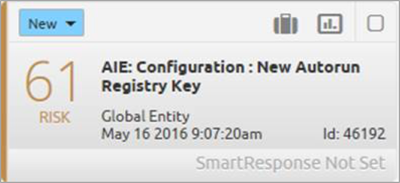
New Auto-Run Registry Key
Figure 7. New Auto-Run Registry Key
Using LogRhythm registry monitoring, native OS auditing or third-party endpoint agents, you can now monitor new registry keys using another powerful feature of AI Engine—a Whitelist Rule Block.
The Whitelist Rule Block can either dynamically learn the normal registry configurations or be provided with a user-defined configuration. In this particular case, if you see new registry keys being created in commonly known locations that are used by ransomware, you’ll detect it.
New Process Excessive File Access
Figure 8. New Process Excessive File Access
Again, using a combination of either LogRhythm endpoint monitoring, native OS auditing or third-party agents, you can detect a never-before-seen process running on an endpoint. You can then keep track of that and detect it if it accesses excessive numbers (1,000s) of files in a short space of time.
This process also uses powerful functionality of the AI Engine. Using a baseline list of known good processes, a threshold rule block to detect excessive file access, and then again using the Loopback feature to connect the dots for these two sets of activities occurring together. In addition, there is also a SmartResponse associated with this alarm that has successfully run—more on that in a second.
Figure 9. AI Engine-Generated Events
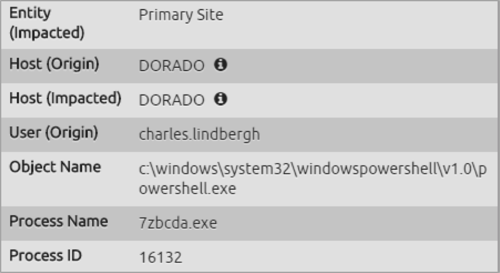
There are two individual AI Engine-generated events that drive the above AI Engine rule. The first looks for the never-before-seen process, 7zbcda.exe, a randomly named process (as often is the case with ransomware).
Figure 10. Inspector Panel for the 7zbcda.exe Randomly Named Process
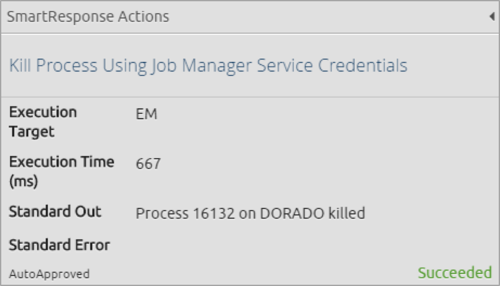
And remember the SmartResponse that was linked to the alarm? Here you can see that LogRhythm successfully terminated that process automatically—not only detecting, but also responding to abnormal activity.
Figure 11: Confirmation of SmartResponse Killing the Process
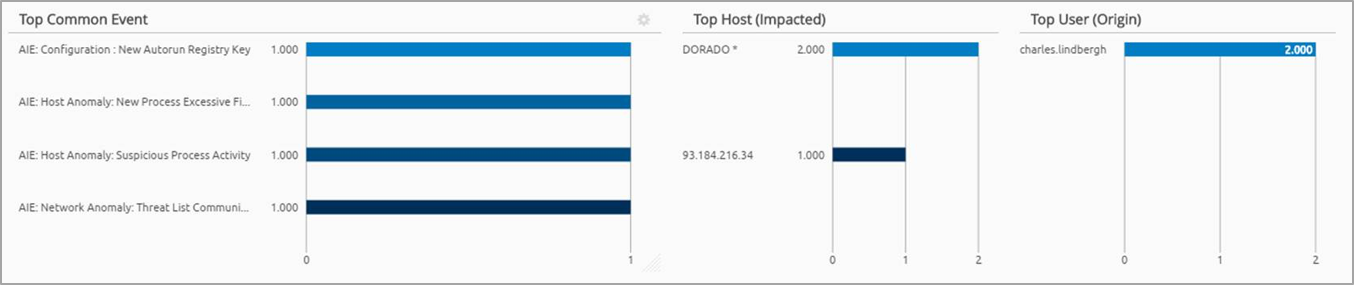
By drilling down into the original ransomware alarm, the high RBP compound alarm, you can see the results via the WebUI drilldown and visually validate all the above activities have taken place, understand the source and impacted hosts and the user (Charles Lindberg).
Figure 12. Top Common Events
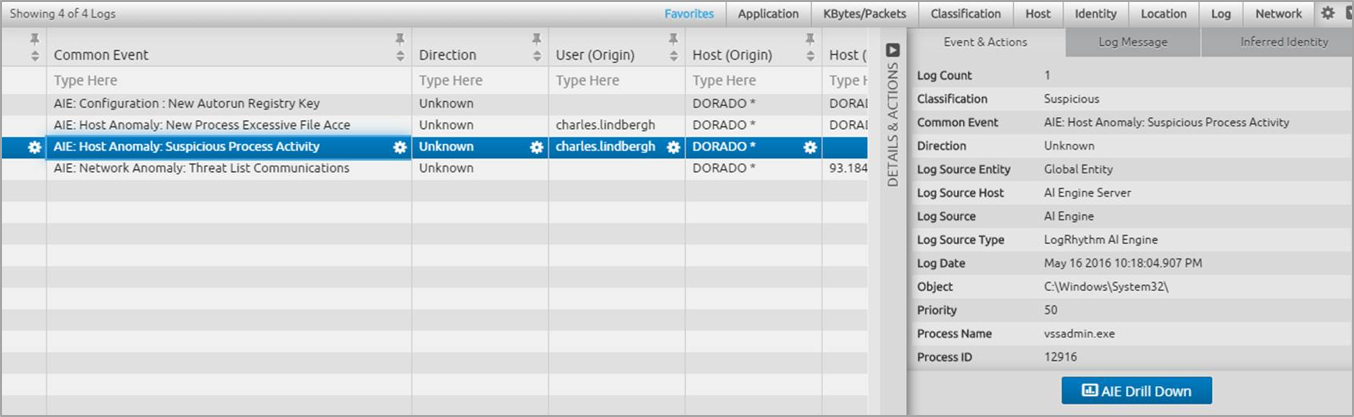
For each of the AI Engine events generated as part of the detecting ransomware behaviors you set up, you can inspect the LogRhythm Gridview to see the related metadata and quickly drill down to bring up the associated raw logs for each event.
Figure 13. Gridview of Metadata
For example, you can seamlessly drill down into each and all of these events, annotating and updating your Case Management as you go. Here are further examples of how quickly you can drill down to this information:
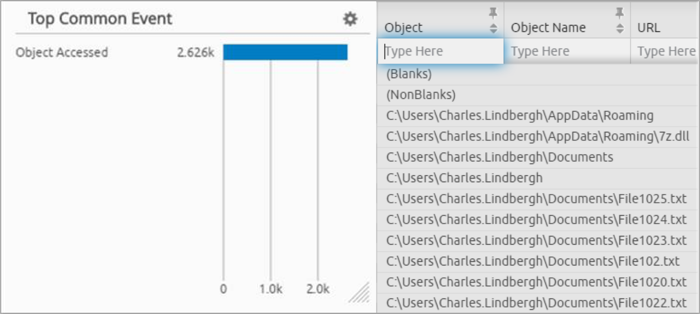
Figure 14. Quickly Visualize the Number of Files Accessed on the Impacted Host
You can quickly visualize the number of files accessed on the impacted host. In this case, in just a few seconds, over 2,600 files were accessed before the LogRhythm SmartResponse automatically terminated the process.
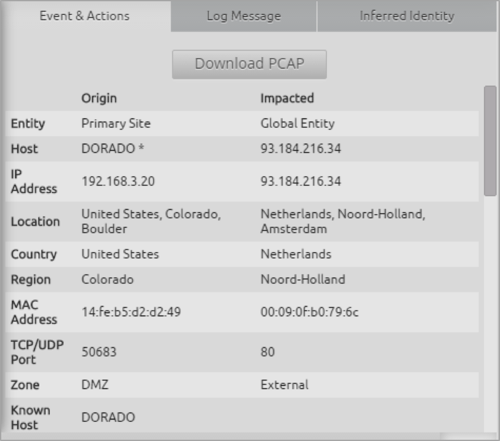
Figure 15. Threat Alarm and Underlying SmartFlow
You can also drill down into the Threat Alarm and see the underlying SmartFlow generated by the LogRhythm NetMon—even downloading the PCAP that includes the full contents of the conversation. And this leads back to your original alarm: Ransomware Behavior.
Figure 16. Original SmartResponse Alarm
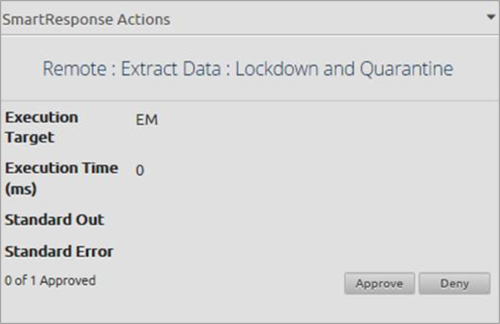
Figure 17. Lockdown and Quarantine Action
This AI Engine Alarm also had a SmartResponse associated with it—LogRhythm Labs’ PS Recon and Endpoint Lockdown. This provides the ability for you to take a forensic capture of a host and isolate it from the network.
Automatic Detection and Response to Ransomware Simplified
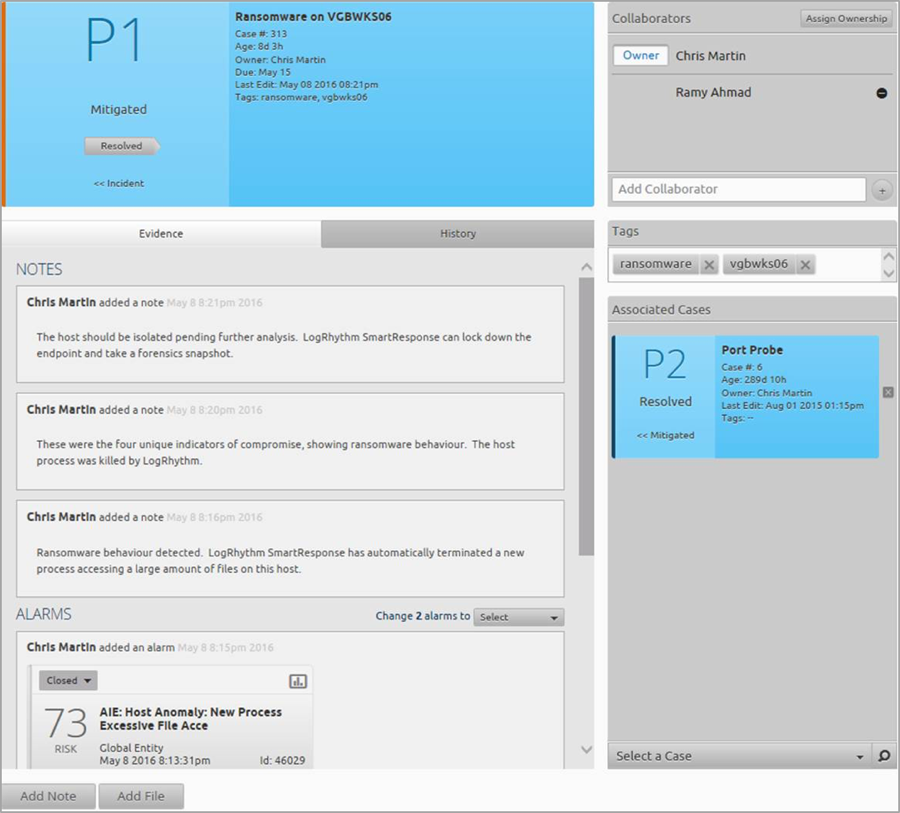
While this is just scratching the surface of what you can do with LogRhythm in the fight against ransomware, you can see how you’ve not only detected ransomware behavior, but you’ve also automatically responded to it—all which is neatly documented in your evidence in Case Management.
Figure 18. Case Management Evidence
To learn more about ransomware and how it works, download our how-to guide on preparing for and detecting an attack.